Discover how EDS is powering discoveries in human health, diagnostics, and personalized medicine.
How enzymatic DNA synthesis works
Three core components make EDS possible:
1. Highly Engineered Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase (TdT DNA Synthesis)
Specialized TdT enzymes, chosen for their unique ability to add diversity during gene recombination, add reversibly-terminated nucleotides to the 3’-end of any single DNA strand with high fidelity and coupling efficiency.

2. Reversibly Terminated Nucleotides

Reversibly terminated nucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs) pause synthesis after a single base addition. These dNTPs are relatively small and rapidly and efficiently restored using mild acidic conditions. They leave no scars, yielding completely natural, molecular biology-ready DNA.
3. Solid Supports and iDNA
A solid support allows for the control of synthesis scale and manipulating the growing oligo strands throughout the EDS process. The solid support has physical and chemical features optimized to enable the synthesis of full-length DNA at a nanomolar scale.
It’s coated with predefined initiator DNA (iDNA) that provides the footprint to initiate template-free DNA synthesis, a cleavage site, coating density that determines synthesis scale, and has been optimized for maximum synthesis yield by minimizing steric hindrance during enzymatic elongation.

The 2-step EDS revolution
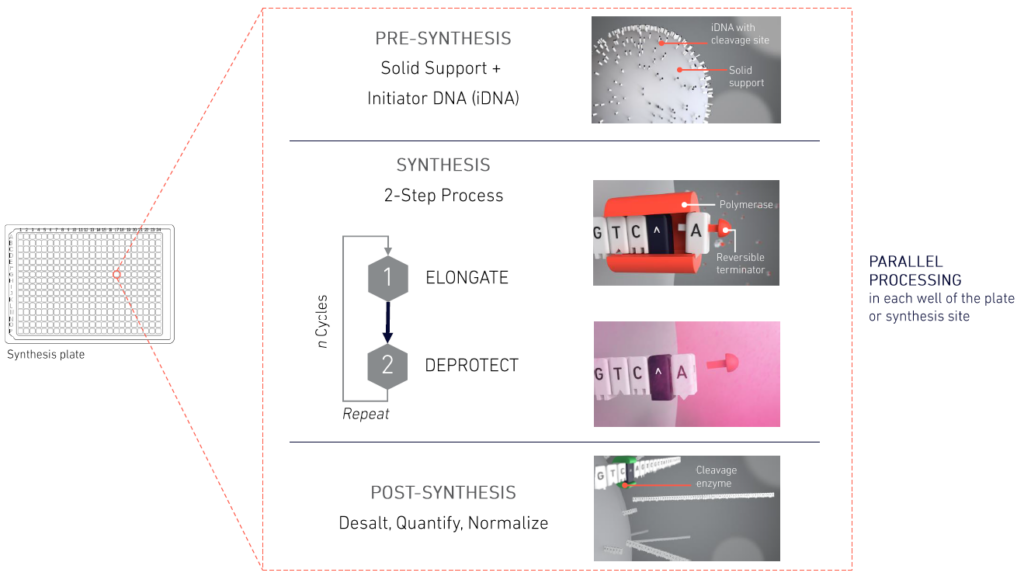
Oligos are enzymatically synthesized in a cyclic, 2-step process:
Step 1. Elongate: The TdT enzyme adds a single nucleotide to the iDNA.
Step 2. Deprotect: The reversible terminator of the nucleotide is removed, leaving the strand ready to be elongated again.
Steps 1 and 2 are repeated until the longest oligo on the plate is completed.
Following completion of the last synthesis cycle, enzymatic cleavage is performed to release oligo sequences downstream from the cleavage site. The resulting oligos are desalted, quantified, and normalized. Molecular biology-ready oligos are collected, immediately ready for the next step of the molecular biology workflow.
